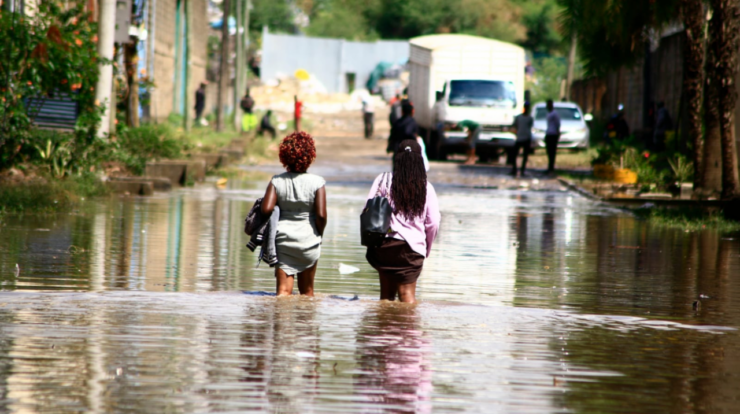
Kenya nairobi flooding – Kenya’s capital city, Nairobi, faces a persistent battle against flooding, a challenge that has plagued the city for years. The city’s susceptibility to flooding stems from a combination of factors, including heavy rainfall, poor drainage systems, urbanization, deforestation, and improper waste management.
These factors have resulted in devastating consequences for Nairobi, including damage to infrastructure, homes, and businesses, disruption of transportation and economic activities, spread of waterborne diseases, and social and psychological impacts on affected communities.
To address the issue, Nairobi has implemented various strategies to mitigate and adapt to flooding, including upgrading and expanding drainage systems, implementing flood warning systems and evacuation plans, promoting sustainable urban planning and development, and raising awareness and educating the public about flood risks.
Case studies of successful mitigation or adaptation measures implemented in Nairobi or other similar urban environments provide valuable lessons for future flood management efforts.
Causes of Flooding in Nairobi
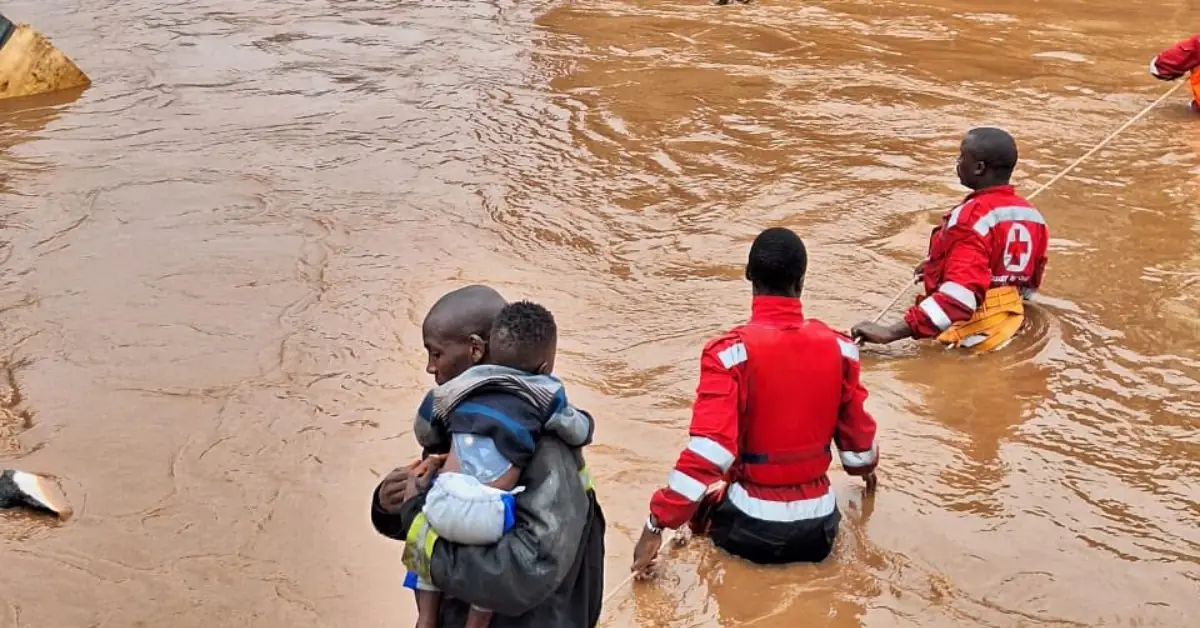

Flooding in Nairobi is a persistent problem that stems from a combination of factors. Heavy rainfall, often exceeding the capacity of the city’s drainage systems, is a major contributor. Urbanization and deforestation have also played a significant role, as the expansion of impervious surfaces reduces water absorption and increases runoff.
Additionally, inadequate waste management practices result in clogged drainage channels, further exacerbating the problem.
Heavy Rainfall and Poor Drainage Systems
- Nairobi receives heavy rainfall during the rainy seasons, with an average annual precipitation of around 800 millimeters.
- The city’s drainage systems are often overwhelmed by the intensity of the rainfall, leading to flooding in low-lying areas.
- Aging and poorly maintained infrastructure further contributes to the problem, as drainage channels become blocked or damaged.
Urbanization and Deforestation, Kenya nairobi flooding
- Rapid urbanization has led to the expansion of impervious surfaces, such as buildings and roads, which reduce water absorption.
- Deforestation in the surrounding areas has also contributed to increased runoff, as trees play a crucial role in absorbing rainwater.
- The loss of natural drainage channels and wetlands further exacerbates the problem, as they provide natural storage and filtration for stormwater.
Lack of Proper Waste Management
- Inadequate waste management practices result in large amounts of garbage and debris accumulating in drainage channels.
- This clogs the channels, reducing their capacity to drain stormwater and increasing the risk of flooding.
- Improper disposal of solid waste also contaminates water sources and poses health risks.
Concluding Remarks: Kenya Nairobi Flooding
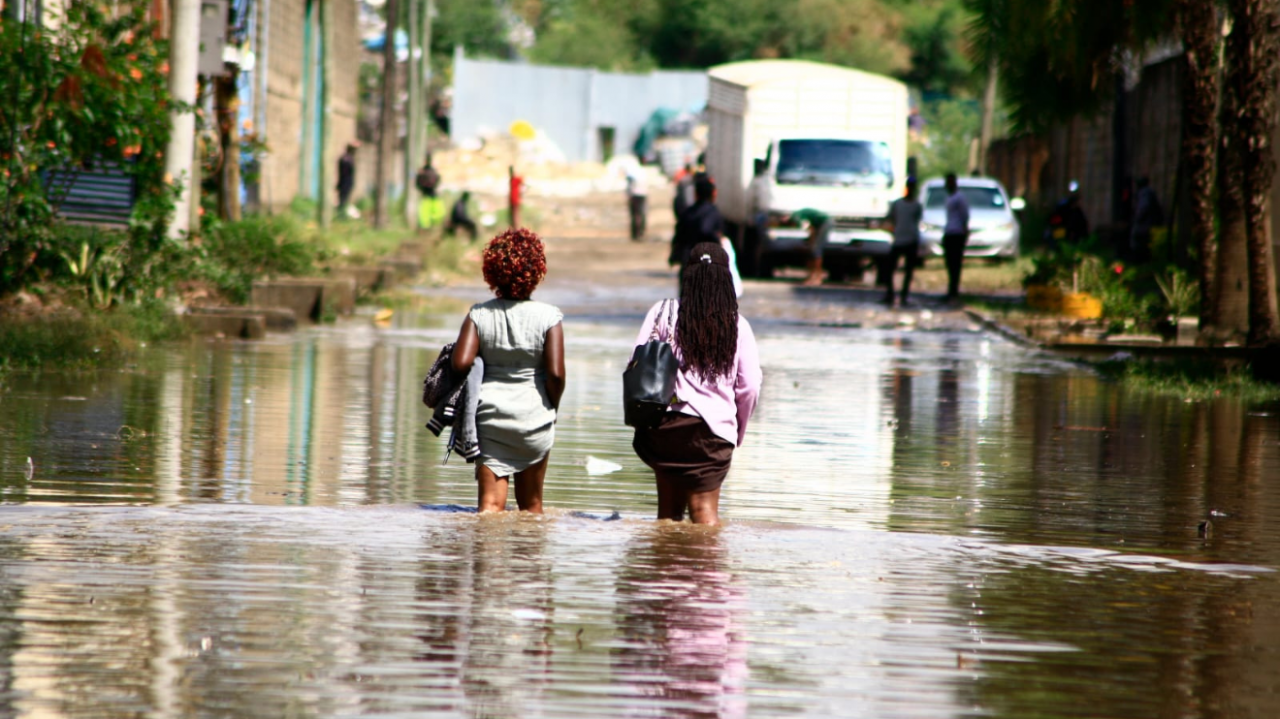

Despite the challenges, Nairobi remains resilient in its efforts to overcome the issue of flooding. The city’s long-term strategy focuses on enhancing its resilience to flooding, exploring innovative solutions, and promoting sustainable practices. By embracing a collaborative approach involving government agencies, community organizations, and the public, Nairobi aims to create a more flood-resilient future for its citizens.
FAQs
What are the main causes of flooding in Nairobi?
The main causes of flooding in Nairobi include heavy rainfall, poor drainage systems, urbanization and deforestation, and improper waste management.
What are the impacts of flooding on Nairobi?
Flooding in Nairobi can cause damage to infrastructure, homes, and businesses, disrupt transportation and economic activities, spread waterborne diseases, and have social and psychological impacts on affected communities.
What measures are being taken to mitigate flooding in Nairobi?
Nairobi has implemented various measures to mitigate flooding, including upgrading and expanding drainage systems, implementing flood warning systems and evacuation plans, promoting sustainable urban planning and development, and raising awareness and educating the public about flood risks.